Deeper Text Understanding for IR with Contextual Neural Language Modeling"
목차
- Author
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Related Work
- Document Search with BERT
- Experimental Setup
- Results and Discussion
- Conclusion
Author
- CMU 박사괴정 (https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~zhuyund/)
- IR에 적용하는 Language Understanding쪽 연구
Three papers in deep retrieval and conversational search got accepted into SIGIR 2020!
 {: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
{: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
Abstract
- 뉴럴넷은 복잡한 언어 패턴과 query-document relation을 자동으로 학습할 수 있는 새로운 가능성을 제공하고 있음
- Neural IR models은 query-document relevance pattern을 학습하는데 좋은 결과를 보여주지만, query 또는 document의 text content를 이해하는 것에 대한 연구는 많지 않았음 (?)
- 본 논문에서는 최근에 제안되었던 contextual neural LM, BERT 등이 IR에서 deeper text understanding에 얼마나 효과 있는지를 알아보고함
- 실험 결과는 전통적인 word embedding보다 BERT가 제공하는 contextual text representations이 더 효과있음을 보여주었음
- BoW retrieval 모델에 비해 contextual LM은 더 나은 language structure를 사용하고, 자연어 형태의 query에 대해 큰 성능향상을 가져올 수 있음
- text understanding ability를 search knowledge와 결합시키는 것은 제한적인 학습셋을 갖는 조건에서 search task를 Ptr BERT가 더 잘할 수 있게 해줌 (정확한해석은 아닌데 대략 이런의미)
Introduction
- Text retrieval은 문서의 의미를 이해하고 search task를 이해하는게 요구됨
- 뉴럴넷은 raw document text와 학습셋으로부터 understanding을 얻어내기 때문에 매력적인 솔루션임
- 대부분의 뉴럴 IR 방법은 query-document relevance patterns을 학습하는데 초점을 맞춤 (다른 말론 search task에 대한 knowledge)
- 하지만 relevance patterns만을 학습한다는 것은 많은양의 학습 데이터를 필요로 한다는 의미이고, 여전히
tail queries나new search domain에 generalize되기 어려움 - Ptr word representation (such as word2vec) 등은 뉴럴 IR에서 많이 사용되어왔음
- 하지만 이런 word co-occurrence 방법론은 text에 대해 shallow bag-of-words 정도의 정보임
- 최근엔 ELMo, BERT 같은 Ptr neural LM 등의 발전이 있었고 기존의 전통적인 word embeddings과 달리 contextual representation을 제공함
- 이런 contextual LM은 전통적인 word embeddings들의 성능보다 뛰어남을 여러 NLP task에서 보여줌
- 이런 모델은 IR에 새로운 가능성을 가져다줌
- 본 논문에서는 BERT를 이용해서 ad-hoc document retrieval 에 적용해봄 (two ad-hoc retrieval datasets에 적용)
- 적은 데이터로 finetuning해도 기존 baseline을 크게 뛰어넘음을 보여줌
- 전통 retrieval models과 다르게
longer natural language queries가short keywords queires보다 좋은 성능을 보여줄 수도 있었음(by large margines with BERT) - 더 분석해본 결과, stopwords, punctuation등 전통 IR 방법에선 무시했던 것들이 문법적 요소와 단어 의존성으로 인해 natural langauge queries를 이해하는데 핵심 역할을 한다는 것도 드러남
- 최종적으로, BERT를 search knowledge from a large search log 로 개선(?)해서 text understanding도 하고 search task도 하게 만듬 (labeled data가 제한적인 경우에 도움됨)
Related Work
- query-document relevance patterns
- approach 1
- text presentations tailored for the search task [1, 2, 9] with search signals from click logs
- pseudo-relevance feedback
- approach 2
- neural architecture로 다양한 matching feature를 잡아내는 것
- exact match
- passage-level signals
- approach 1
- 위와 다르게, query/document의 text content를 어떻게 이해하는가에 대한 연구는 많이 없는 상태임
- 사용해도 word2vec 정도였음
- BERT가 잘되니 적용해보겠음 (open-domain document에 학습하다보니 general pattern 학습함)
Document Search with BERT
 {: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
{: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
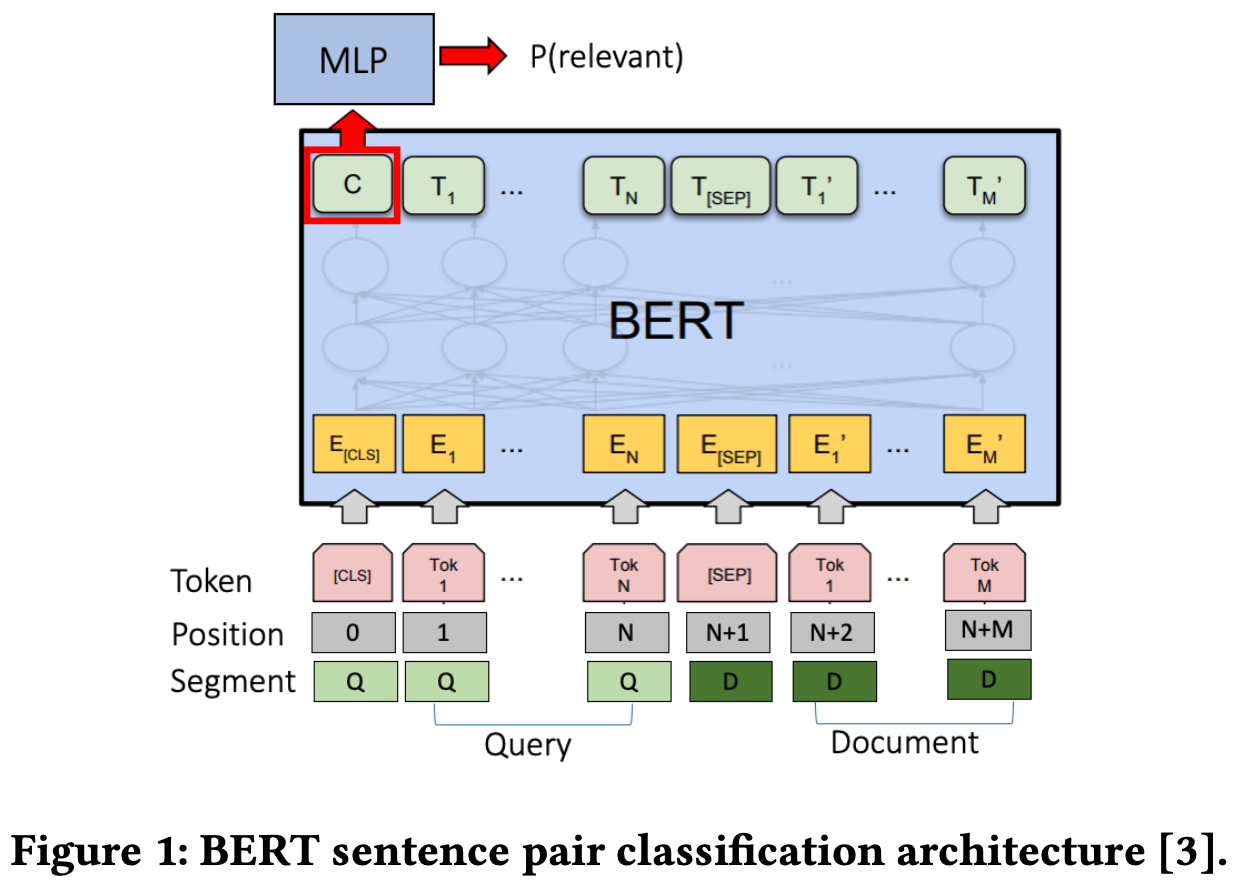
- 본 논문에서는 off-the-shelf BERT architecture를 사용
- sentence pair classification architecture를 의미
- 마지막 레이어에서 binary classification을 통해 relevance의 확률을 예측함
Passage-Level Evidence
- BERT를 긴 문서들에 적용하면 메모리와 복잡도 등이 증가하게됨
- senence-trained model이니 long text에 효과가 덜할 수도 있음
- 이 때문에 문서를 overlapping passages로 나눔
- neural ranker는 각각의 passage에 대해 독립적으로 relevance를 예측함 (같은 문서지만 쪼갰으니 여러번 계산하는 듯..?!)
- document score is the score of
the first passage (BERT-FirstP), the best passage (BERT-MaxP), or the sum of all passage scores (BERT-SumP)
Augmenting BERT with Search Knowledge
- search task는 다음 두가지를 모두 요구함
- general text understanding
- e.g. Honda is a motor company
- more-specific search knowledge
- e.g. people want to see special offers about Honda
- general text understanding
- BERT는 genral langauge patterns을 배우긴 했지만, search knowledge는 labeld search data로부터 학습해야만함
- 이런 종류의 데이터는 매우 expensive하고 모으는데 시간이 걸림
- 이는 pre-trained ranking model (언어 이해지식과 검색 지식 모두 갖고 있는) 을 요구하게함
- BERT를 large search log 를 통해 튜닝해서 search knowledge를 포함하도록 augmentation함
- 이렇게하면 데이터가 검색에서 적은 케이스에 도움이 될 것으로 기대함
Experimental Setup
Datasets
- Robust04
- news corpus (article, ptr corpus에 가까움)
- 0.5M documents and 249 queres
- 두가지 버전의 queries로 구성됨
- short keyword query (title)
- longer natural language query (description)
- relevance assessment에 대한 narrative 포함
- ClueWeb09-B
- web pages (tables, navigation bars, discontinuous text)
- 50M web pages and 200 queries
- For augmenting BERT with search data, we follow the domain adaptation setting from Dai et al. [1] and use the same Bing search log sample. The sample contains 0.1M queries and 5M query-document pairs.
 {: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
{: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
- Robust04
Baselines and Implementations
- Unsupervised baselines
- Indri’s bag of words (BOW)
- sequential dependency model queries (SDM)
- Learning-to-rank baselines
- RankSVM
- Coor-Ascent with bag-of-words features
- Neural baselines
- DRMM
- word2vec 사용함
- 2개의 데이터셋에선 성능이 젤 잘 나왔던 neural models임
- Conv-KNRM
- n-gram embeddings for search task
- large search log로 학습할때 좋은 성능 나옴
- Bing search log 이용해서 만들면 SOTA임 (
근데 왜 표엔 없지)
- DRMM
- baseline들은 stopword 지우고 stemming 했지만 BERT는 raw text 사용함
- Supervised models은 BOW with 5-fold cross-validation을 사용해서 검색된 top 100 documents를 re-rank함 (
정확히 어떻게 한다는거지)
- Unsupervised baselines
Results and Discussion
Pre-trained BERT for Document Retrieval
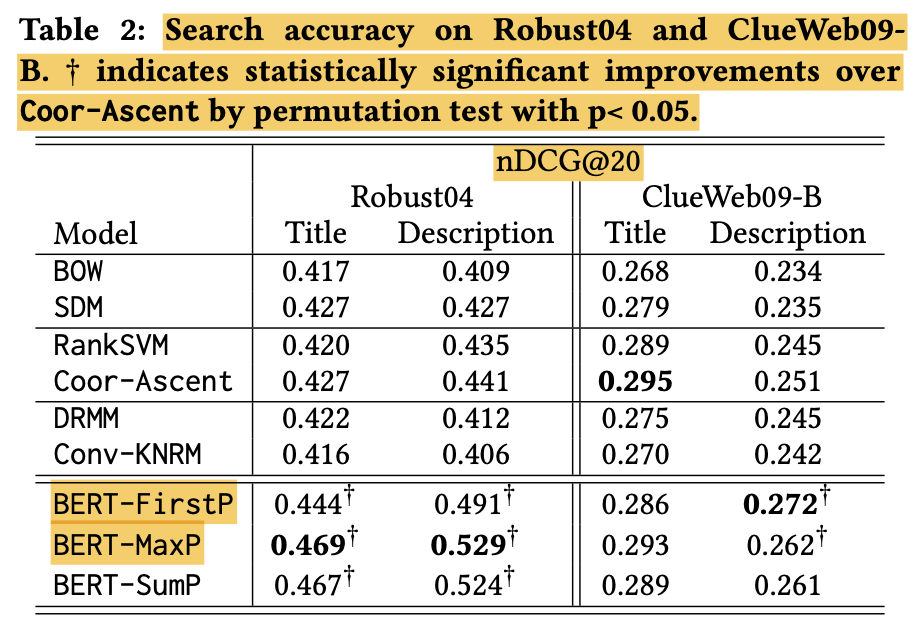
- Robust04에서 BERT는 지속적으로 베이스라인보다 tite query에 대해서는 10% margin으로 description query에 대해서는 20% margin으로 더 나은 성능을 보여줌
- ClueWeb09-B에서는 BERT는 Coor-Ascent와 title query에서는 비슷하지만 description query에서는 더 좋은 성능을 보여줌
- 위 결과를 종합하면 description queries에서는 BERT가 효과가 있음
 {: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
{: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
Sources of effectiveness
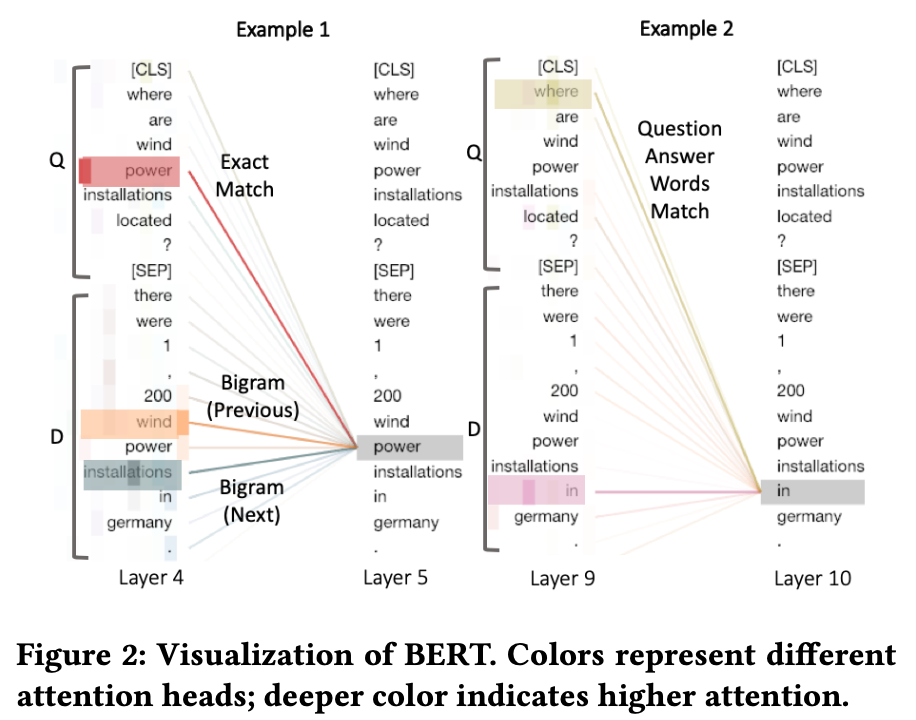
- two layers from the BERT-MaxP model when predicting the relevance between a description query ‘Where are wind power installations located?’ and a sentence ‘There were 1,200 wind power installations in Germany’
- layer에서 exact match, Bigram (prev, next) 등을 학습한 걸 볼 수 있음
- where-in 매칭은 context를 고려한다고 할 수 있음 (전통 IR에서는 이런 단어들은 무시함 (IDF가 낮아서))
- 이런걸 보면 stopwords도 사실 relevance에 중요한 단서가 될 수 있음을 보여줌
 {: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
{: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
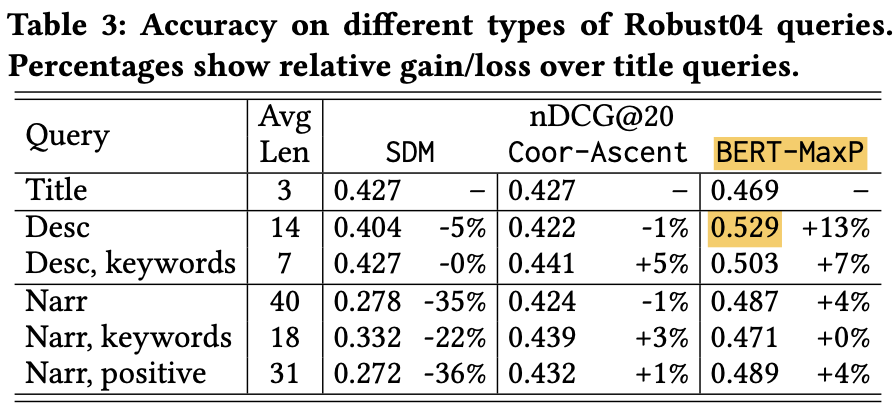
Title queries vs. description queries
- 정리하면, description queries가 title queries를 이번 연구처럼 large margin을 갖고 이긴게 거의 처음임
- On Robust04, using description queries with BERT-MaxP brings a 23% improvement over the best title query baseline (SDM)
- Most other ranking methods only get similar or worse performance on descriptions compared to titles. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time we see that description queries outperform title queries with such a large margin
Understanding Natural Language Queries
- 3가지 종류의 질의로 text understanding을 검사함
- title
- description
- narrative (removing stopwords and punctuation)
BERT-MaxPmakes large improvement on longer queries by modeling word meaning and context.
 {: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
{: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
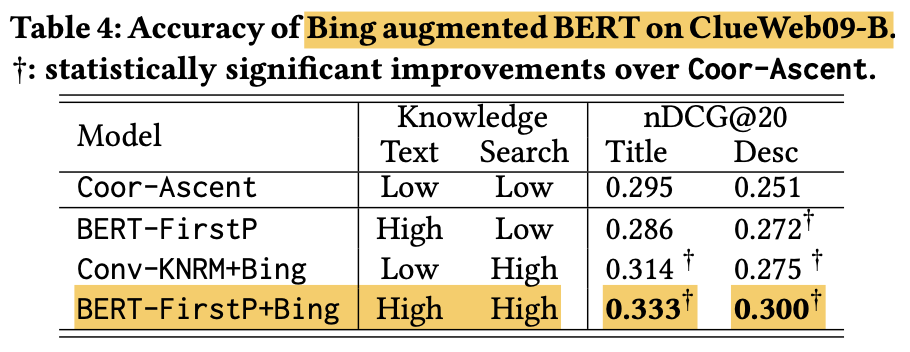
Understanding the Search Task
- Corpus-trained text representation이 꼭 search task와 align되는건 아님
Its pre-trained language model encodes general word associations like (‘Honda’, ‘car’), but lacks search-specifc knowledge like (‘Honda’, ‘special offer’)- search specific knowledge가 요구됨
- 데이터가 부족할 수 있음 이걸 해결해야함
- if BERT’s language modeling knowledge can be stacked with additional search knowledge to build a better ranker, and if
the search knowledge can be learnedin a domain-adaptation mannerto alleviate cold-start problems - BERT를 Bing search log with 0.1M queries 샘플에서 학습시키고 ClueWeb09-B에 finetuning시킴
결과적으로 Bing search log로 학습하면 성능이 더 개선됨
 {: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
{: height=”50%” width=”50%”}
Conclusion
- Text understanding is a long-desired feature for text retrieval
- Contextual neural language models open new possibilities for understanding word context and modeling language structures
- BERT가 search task에서 적용 잘되고 성능도 높여줌
We found that queries written in natural language actually enable better search results when the system can model language structures
Deeper Text Understanding for IR with Contextual Neural Language Modeling"